LOSS OF TOOTH ENAMEL DUE TO ACID ATTACK IS KNOWN AS EROSION.
Enamel is the hard outer layer, protective coating of the tooth, which protects the sensitive dentine. When the enamel is worn away, the dentine underneath is exposed, which may lead to pain and sensitivity.
What causes erosion?
- Excessive soft drink consumption (high level of phosphoric and citric acids)
- Fruit drinks (some acids in fruit drinks are more erosive than battery acid)
- Dry mouth
- Acid reflux disease (GORD)
- Medications (aspirin, antihistamines)
- Genetics (inherited conditions)
- Environmental factors (friction, wear and tear, stress, and corrosion)
Types of tooth erosion
Tooth erosion is caused by friction, wear and tear, stress, and corrosion or any combination of these actions. The mechanisms include:
- A natural tooth-to-tooth friction happens when you clench or grind your teeth such as with bruxism, often occurring involuntary during sleep.
- A physical wear and tear of the tooth surface that happens with brushing teeth too hard, improper flossing, biting on hard objects (such as fingernails, bottle caps, or pens), or chewing tobacco.
- Stress fractures in the tooth such as cracks from flexing or bending of the tooth.
- Chemically when acidic content contacts the tooth surface such as with certain medications like aspirin or vitamin C tablets, highly acidic foods, GORD, and frequent vomiting from bulimia or alcoholism.
Management of sensitivity due to erosion
Sensitivity can be managed by a wide variety of procedures, agents and formulations which are applied either ‘in office’ or ‘at home’. There are two main desensitizing techniques are used in the treatment of Sensitivity:3
- Desensitizing by occluding the dentinal tubules by formation of smear layer on the exposed area. The agents used in this technique are calcium hydroxide, hydroxyapatite, silver nitrate, strontium chloride, by means of using hard tissue lasers or fluoride iontophoresis
- Desensitizing by blocking the pulpal sensory nerves with agents like silver nitrate in various forms.
In-office desensitizing agents
The in-office desensitizing therapy provides an immediate relief from Sensitivity. In-office desensitizing agents include glass ionomer cement, composites, varnishes, oxalates etc.
At home desensitizing agents
The requirements for an ideal dentine desensitizing agent have been listed by Grossman which includes:
- Rapidly acting with long-term effects
- Non-irritant to pulp
- Painless and easy to apply
- Should not stain the tooth
The traditional therapy for the management of Sensitivity is primarily aimed at occluding the dentinal tubules or making coagulates inside the tubules. Patients are frequently prescribed with over-the counter desensitising agents. At home desensitizing agents include toothpastes, mouthwashes and chewing gums.4
Desensitizing toothpaste
Many desensitizing toothpastes contain potassium salts, sodium fluoride, strontium chloride, dibasic sodium citrate, formaldehyde, sodium monofluorphosphate and stannous fluoride. The desensitising toothpastes should be used with toothbrush with soft bristles. Patients are advised to use less water to avoid dilution of the active ingredient.4
Desensitizing toothpastes are most widely used home treatment for the management of Sensitivity. Nano-technology has been advancing; nano-particles of hydroxyapatite are incorporated in dentifrices which occlude the dentinal tubules by its smaller particle size.3
Efficacy of Nano-hydroxyapatite in the management of Sensitivity
Reddy S et al, conducted a study to assess the efficacy of pro-argin technology and nano technology in the management of Sensitivity.5
The study was conducted in 30 patients with at least 2 sensitive teeth with a verbal rating scale (VRS) of >5 post air blast stimulation. The patients were divided into 2 groups Group 1 received toothpaste with pro-argin technology and Group 2 received toothpaste with nano-hydroxyapatite technology. These patients were subjected to cold water and air blast stimulation for Sensitivity assessment at baseline and after 3 days using VRS scores.5
The study results demonstrated that there was a significant rapid relief in patients using toothpaste with nano-hydroxyapatite.5
An in vitrostudy was conducted to compare the dentifrice with nano-hydroxyapatite (Aclaim) versus pro-argin technology. The study showed that nano-hydroxyapatite containing dentifrice led to a high degree of tubule occlusion after just 2 minutes and was five times faster than the occlusion rate observed in pro-argin technology (Fig 2).2
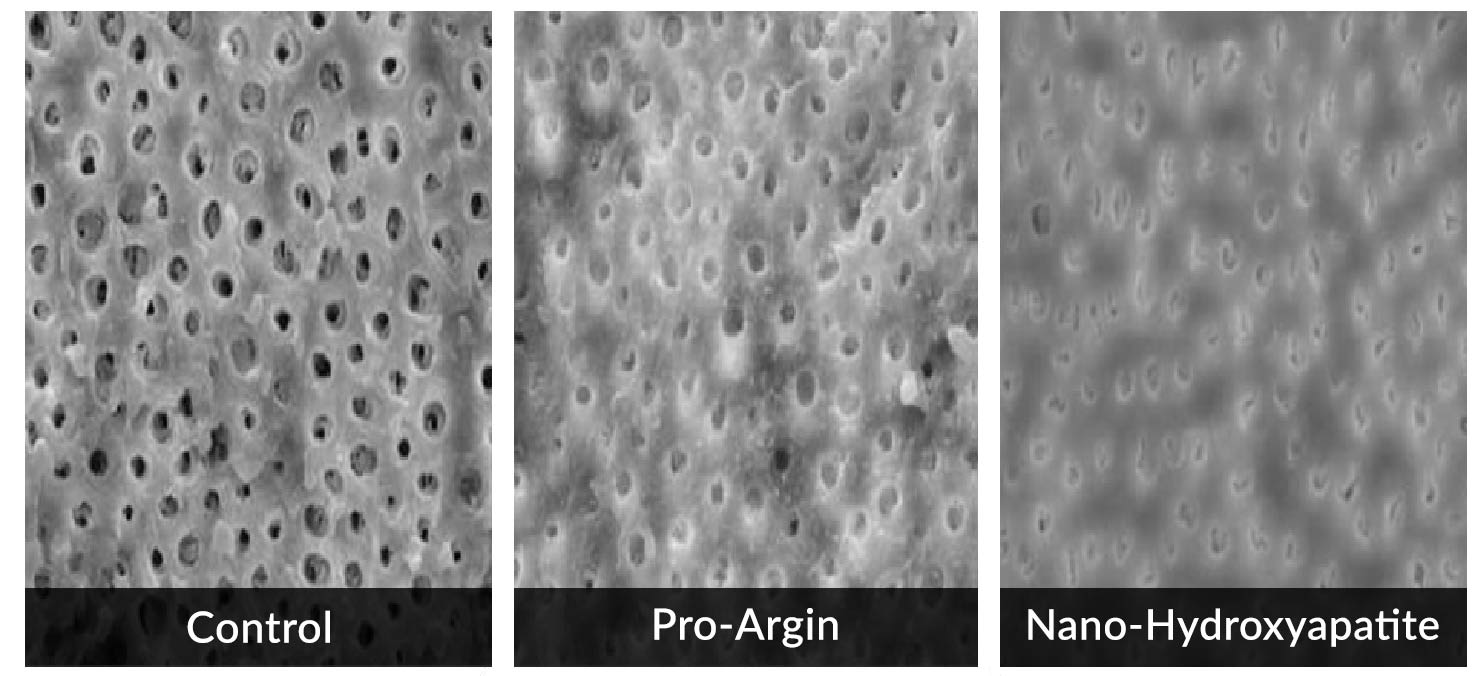
An in vivo clinical study was conducted involving 45 patients to evaluate the efficacy of toothpaste containing nano-hydroxyapatite (Aclaim), potassium nitrate and propolis in management of Sensitivity. Propolis is a natural, non-toxic resin which can occlude dentin tubules and decreases their permeability, while potassium nitrate reduces dentinal sensory activity. Patient’s Sensitivity was tested using visual analog scale for pain before and after using the dentifrices. Figure 3 shows the results after one and four weeks of treatment.2
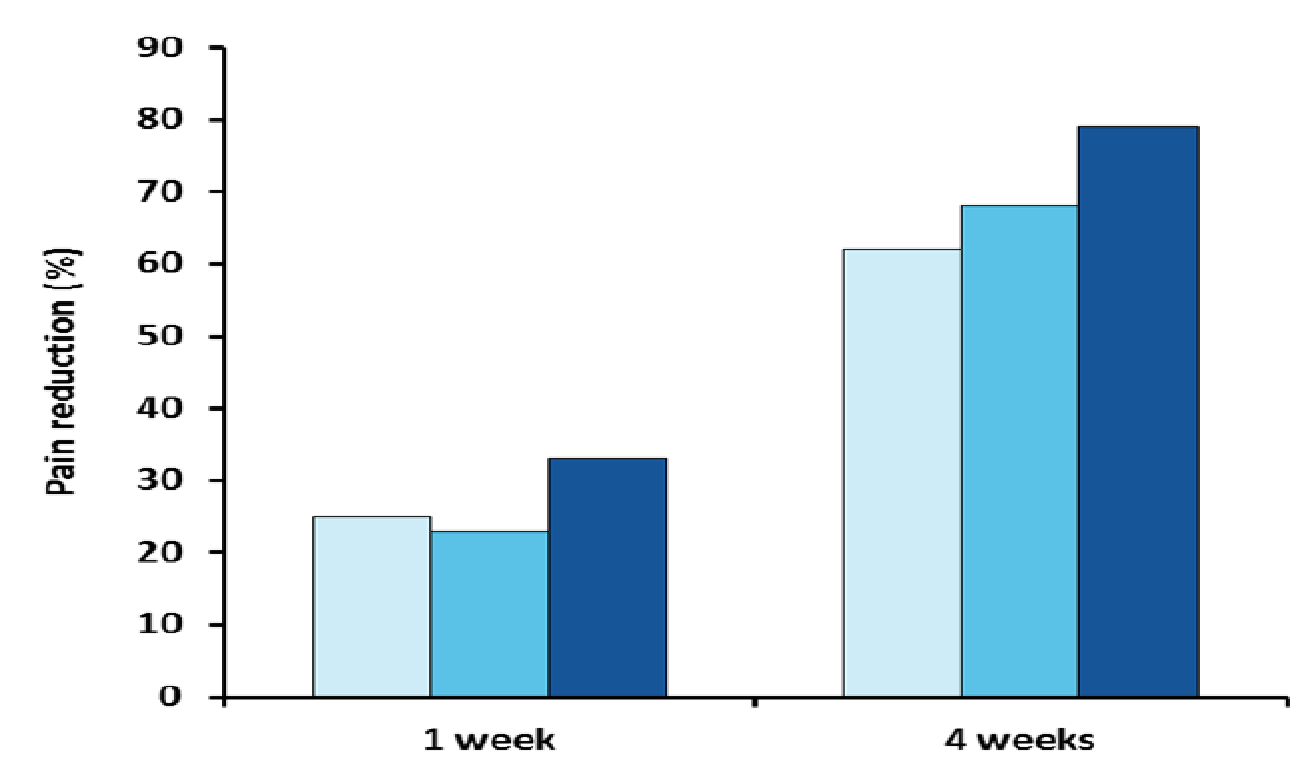

Fig. 3 Reduction of dental hypersensitivity after treatment with potassium nitrate, Propolis and Aclaim during one and four weeks
Nithin G et al, conducted a randomized, double-blind, parallel arm study to assess and compare the effectiveness between nano-hydroxyapatite and a benchmark dentifrice in reducing Sensitivity.
The study included 36 patients who were randomly assigned with two dentifrices group 1 with nano-hydroxyapatite (Aclaim) and Group 2 with 5% calcium sodium phosphosilicate. The patients were evaluated clinically using three different stimuli including tactile, cold water and air blast. The patients’ response was evaluated at baseline and after 4 weeks.The toothpaste containing hydroxyapatite was effective in reducing Sensitivity and hence can be recommended in the management of hypersensitivity.6
Conclusion
Enamel is the hard outer layer, protective coating of the tooth, which protects the sensitive dentine. When the enamel is worn away, the dentine underneath is exposed, which may lead to pain and sensitivity. Sensitivity can be managed by a wide variety of procedures, agents and formulations which are applied either ‘in office’ or ‘at home’.Desensitizing toothpastes are most widely used home treatment for the management of Sensitivity. Nano-technology has been advancing; nano-particles of hydroxyapatite are incorporated in dentifrices which occlude the dentinal tubules by its smaller particle size.3 Evidence suggests that toothpastes containing nano-hydroxyapatite are effective at occluding dentin tubules and reducing Sensitivity.2
References
- Causes & Treatment of Tooth Erosion. Available at: https://gpdentalpartners.com.au/education/causes-treatment-of-tooth-erosion/
- Effectiveness of nanoXIM•CarePaste on dentin tubule occlusion and enamel remineralization. Available at http://fluidinova.com/docs/effectiveness_of_nanoxim_carepaste_on_dentin_tubule_occlusion_and_enamel_remineralization.pdf . Accessed on 14 September 2018.
- Amin M, Mehta R, Duseja S, et al. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Commercially Available Nano-Hydroxyapatite Paste as a Desensitizing Agent. Adv Hum Biol. 2015;5(1):34-38.
- Miglani S, Aggarwal V, Ahuja B. Dentin hypersensitivity: Recent trends in management. J Conserv Dent. 2010 Oct;13(4):218-24.
- Reddy S, Prasea MGS, Prasad S, et al. The effect of pro-argin technology vs nano technology using commercially available dentifrice: A comparative study. International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences 2014; 1(1): 26-30.
- Gopinath NM, John J, Nagappan N, et al. Evaluation of Dentifrice Containing Nano-hydroxyapatite for Dentinal Hypersensitivity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Int Oral Health. 2015 Aug;7(8):118-22.


